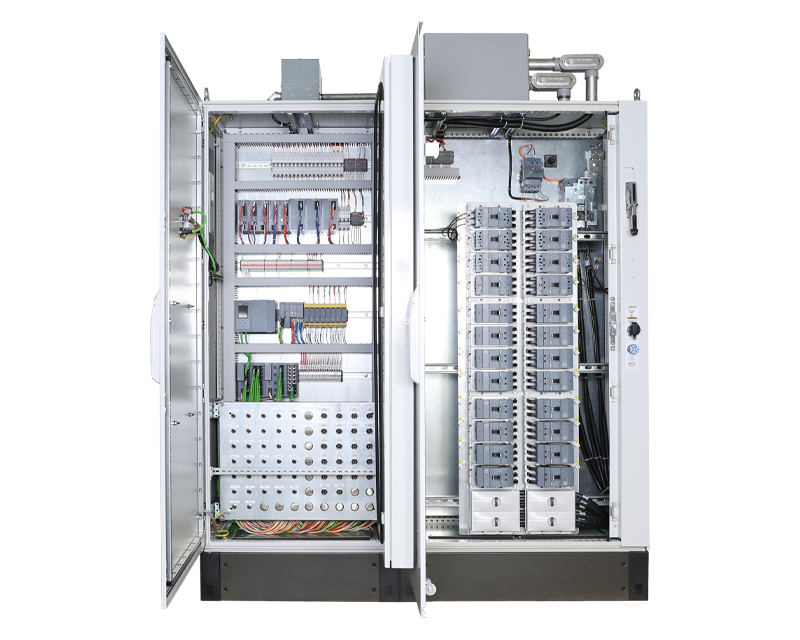
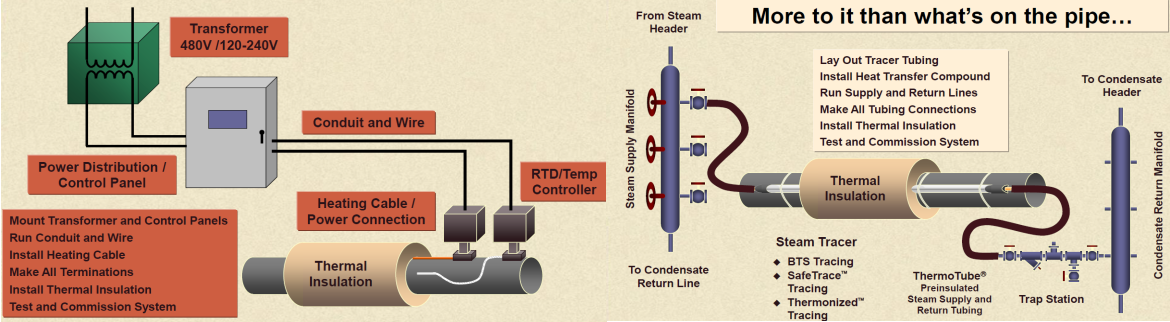
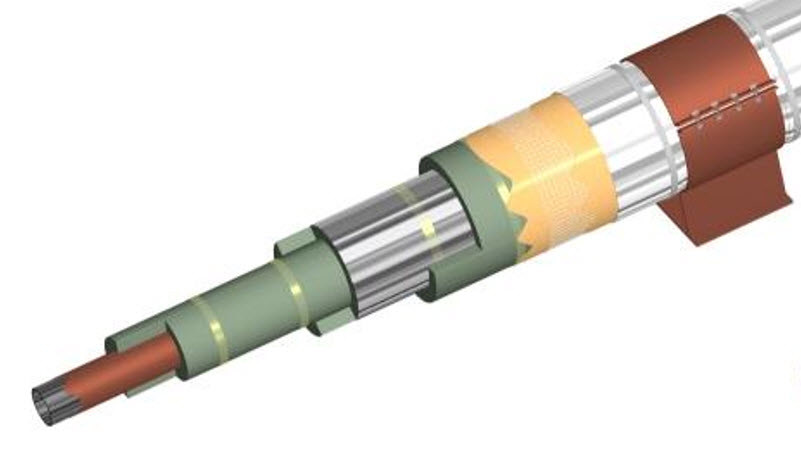
Thermal monitoring systems are generally applied to keep the product stationary in the chamber at a certain temperature. Vapor is the phase change of a liquid into a gas. It contains high energy. Today, steam thermal monitoring systems are used more than electric thermal monitoring systems in plants. The main reason for their higher use is that there is a surplus of steam in the plants and the relative low investment cost. However, they have several disadvantages and are usually not included in operating costs. The main ones are that it requires frequent maintenance, is less operational, and damages other systems in case of failure. In addition, steam thermal monitoring systems cannot be monitored and do not allow keeping records of past operating status. High energy content makes them ideal for systems that require high energy. Examples include systems that transfer or store asphalt. Electrical thermal monitoring systems can be monitored, do not fail and have a lifetime of around 35 years. They consume very low energy with appropriate control mechanisms. Investment costs are higher than steam systems.
In summary, the decision on whether to implement electric or steam thermal monitoring in any system should be taken after a detailed engineering study. Otherwise, it will cause financial loss as investment cost or operation cost.